Chaos engineering is a term that refers to creating chaos within a system at different levels to test the resiliency of the complete stack, thereby identifying resiliency gaps within it. With rapid adoption of cloud providers and their attendant services, microservices, and other tools/technologies, there is an increased need to test the resiliency of those systems to ensure the application remains uninterrupted. Even in cases where there are cloud, tools, or application disruptions, the system is able to continuously deliver expected level of service without degrading customer experience.
Ideally, testing the resiliency of the system should be part of the design itself.
Nagarro’s Continuous Resiliency Testing (CRT) accelerator helps you automate resiliency and reliability testing directly via your CI/CD pipeline. Once integrated with design, it should be automated within the DevOps framework to continuously check for resiliency gaps and continuously fix them. Compatible with all the leading chaos engineering tools, the accelerator helps expedite your journey to building a reliable and resilient application.
Chaos engineering orchestration with DevOps
To execute the resilience strategy that we discussed above, DevOps tools/technologies can help automate the complete lifecycle of setting up the chaos platform. This can be done using enterprise or open-source tools such as Jenkins, Gitlab, and leading chaos tools. Reporting them to a wide audience, this complete process can be integrated with CI/CD pipeline to ensure smooth continuous execution.
So, subsequently, continuous chaos will be a part of CI/CD pipelines. This is done to execute the resilience strategy for an environment during deployment itself, thereby rectifying any environment issues.
We have multiple chaos engineering tools available. And each tool has its own strength with respect to features available, attacks, automation support, environment support, usability, enterprise support, and so on. Based on these strengths, we should select a tool which serves our purpose of testing the in-depth resiliency at each level of the environment.
Let’s explore some of the leading chaos engineering tools with their practical usability and support with respect to environments.
- Gremlin
- Harness
- Chaos Blade
- Chaos Mesh
- LitmusChaos
- Azure Chaos Studio
- AWS Fault Injection Simulation
1. Gremlin:
- Developed by: Kolton Andrus
- Platform(s): Cloud, VMs (Virtual Machines), Bare Metal Servers, Kubernetes, container, etc.
Gremlin is a SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) based chaos engineering tool, sometimes referred to as CaaS (Chaos-as-a-Service), which provides a set of attacks related to system resources, states, and networks to test the resiliency of the systems. Gremlin provides three sets of attacks, but it is the user’s responsibility to determine which attack best suits the environment and how multiple tests can be clubbed together to test the resiliency of the complete environment. Gremlin provides some level of attacks to free tier accounts, but to access Gremlin’s full range of capabilities there is a licensing cost.
As a prerequisite, Gremlin requires installing a proprietary agent in the server/container/pods of the environment. It provides different kinds of attacks at resource, state, and network levels, which can be clubbed together for testing the specific resilience scenarios.
Gremlin provides support for servers (cloud or Bare Metal), Containers and Kubernetes clusters, and supports three means of interactions (i.e., UI, APIs, and through command lines).
When to use it:
Gremlin combines many features of Simian Army tools to create a common platform that can be used to test the resilience of the system. It provides great automation support with CLI, UI, and API, so that all attacks can be automated with CI/CD itself. Gremlin is great for SaaS implementations where teams must evaluate resiliency on a variety of parameters. It offers strong integrations with multiple public clouds, Kubernetes clusters, and offers strong automation support.
Pros:
- Comes with many built-in attacks related to network, resource, cluster, container, etc. UI provides all configuration levels
- Detailed documentation
- Automation support
Cons:
- Includes a license cost to access full functionality
- Non-customizable
- Limited reporting capabilities
2. Harness Chaos Engineering Tool
- Powered by: Litmus
- Platform: Kubernetes
Harness Chaos Engineering tool enables DevOps and SRE teams to collaborate and run chaos tests that go beyond traditional unit, integration, and system tests to identify any reliability issues. The tool provides custom integration to CI/CD, GitOps and application performance monitoring & observability tools. It also provides enterprise dashboards, analytics, and reports to ensure alignment of key metrics.
When to use it:
Designed for cloud-native systems, Harness Chaos Engineering tool can be added to CI/CD pipelines for continuous reliability validation to protect production environments from downtime. It covers 48 75+ real-world failure experiments through Enterprise ChaosHub to enable reliable deployments and less downtime. The tool can orchestrate chaos engineering experiments automatically in the software delivery pipeline.
Pros:
- Provides enterprise-grade security and privacy controls of all experiments and their results through support for self-hosted, on-premises, and air-gapped deployments of CE.
- Supports fully private chaos experiment repos to contain the experiments.
- Enables teams to run repeatable events with multiple experiments through its GameDay feature.
- Provides resiliency score to measure improvements as well as automate experiment analysis & results.
Cons:
- Licensing cost
3. Chaos Blade
- Developed by: Alibaba
- Platform(s): Docker, Kubernetes, Bare Metal, cloud platforms
Chaos blade is an open-source chaos engineering tool designed to improve fault tolerance of systems and ensure business continuity. It provides support for the following levels of attack:
a) Resource Level (Cloud, VM, Docker): CPU, Memory, Network, Disk, etc.
b) C++ Application Level: Specifying arbitrary methods, code injection delays, tampering with variable and return values.
c) Java Application Level: Specifying class methods to inject various complex experimental scenarios.
Chaos Blade comes up with different sets of operators to create chaos attacks on different levels of environments (e.g., cloud, containers, OS, Java, etc.). Installation of these operators are prerequisite for creating any chaos within the system.
Chaos Blade covers a vast number of attacks and platforms, but it lacks reporting and the ability to schedule those attacks. It does provide documentation, but only in standard Chinese.
When to use it:
With Chaos Blade, resilience can be tested at the infra and code levels. As a result, Chaos Blade is the ideal tool for teams looking to test resilience at the code level and those look to check code maturity, with application fault injection, and thereby check the complete system’s resiliency.
Pros:
- Support for application/code-level attacks
- Quick and easy setup
- Include a vast variety of attacks with regards to Kubernetes
- Automation support
Cons:
- No UI Support
- Not customizable
- Only provides documentation in Chinese
4. Chaos Mesh
- Developed by: PingCAP
- Platform(s): Kubernetes
Chaos Mesh is an open-source Kubernetes native chaos engineering tool designed to test resiliency with different level of attacks. It also provides a UI to perform those attacks and check on the blast radius with some of the configuration settings.
Chaos Mesh provides support for attacks such as network latency, system time manipulation, kernel panics, Disk I/O, and others.
When to use it:
Chaos Mesh is ideal for teams looking for fine-grained attacks with respect to Kubernetes components and for those looking to test resilience at each of those component levels. Chaos Mesh also allows teams to tune the blast radius based on Kubernetes selectors and labels.
Pros:
- UI with many configurations
- Support for a large number of attacks
- Automation support
Cons:
- No ability to schedule attacks
- No support for access controls within the UI
The downside of Chaos Mesh is that it provides very limited/negligible support for testing resiliency of VMs or Bare Metal servers. It also does not provide any mechanism to define the attack duration from within the UI itself.
Tailored Solutions: While most solutions offer a fixed set of attacks with a fixed set of environment support, Nagarro’s in-house chaos framework comes with a large number of attacks and the flexibility to add/modify attacks with respect to environment and applications.
5. LitmusChaos
- Developed by: MayaData
- Platform: Kubernetes
LitmusChaos is an open-source chaos engineering platform. It is a Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) hosted project like Chaos Mesh. It provides several experiments for testing containers, Pods, and nodes. It also provides a centralized public repository of experiments called ChaosHub to which anyone can contribute.
When to use it:
Litmus is a wide-ranging tool that offers several useful attacks and monitoring features. However, it requires a multi-step process that includes setting permissions and annotating deployments to run an experiment. While there are workflows to support the process, especially when used through the Litmus Portal, it is complex. A few features also don’t appear in the documentation and are only available through the project’s GitHub repository.
Pros:
- An extensible platform that integrates with other tools for custom experiments
- Web UI has a dashboard and provides resilience scores as per successful workflows
- ChaosHub hosts several experiments
- Provides automated system health checks with Litmus Probes
Cons:
- The process is difficult and lengthy to run experiments.
- Permissions are assigned for each chaos experiment, making it difficult to track and manage access
6. Azure Chaos Studio (Preview)
- Powered by: Microsoft
- Platform(s): Azure
Azure Chaos Studio Preview is a fully managed chaos engineering experimentation platform to find potential weaknesses proactively, from late-stage development to production. It supports agent-based faults and requires a Chaos Studio agent as part of a VM build or service-direct.
When to use it:
Improve your understanding of application resiliency by conducting controlled experiments on Azure applications, exposing them to actual or simulated faults. Observe and analyze how the applications respond to real-world disruptions, including scenarios like network latency, unexpected storage outages, etc.
Pros:
- Provides a continuously expanding library of faults that includes resource pressure, network latency, blocked resource access, infrastructure outages, etc.
- Provides experiment templates to make it easier for users to start with chaos engineering
- Enables users to integrate load testing into chaos experiments to simulate real-world customer traffic
Cons:
- Supports Azure applications only
- Available in a preview state with no exact release date
- No recommended experiments or templates are available
7. AWS Fault Injection Simulator (FIS)
- Powered by: Amazon Web Services
- Platform(s): AWS
AWS Fault Injection Simulator (FIS) is a service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that enables users to perform fault injection testing in a controlled manner on AWS resources such as Amazon EC2 instances, Amazon RDS databases, and more.
When to use it:
As a fully managed fault injection service, AWS FIS makes it easier for users to identify weaknesses of an application to improve performance and resiliency.
Pros:
- Prebuilt templates to set up and run chaos experiments
- Insights by generating real-world failure conditions
Cons:
- Native to AWS only
- Limited number of attacks
- Difficult to run an attack as it requires IAM roles, targeting specific AWS resource IDs, and creation of SSM Documents
High-level comparison of chaos engineering tools based on current functionalities:
|
Tools |
Environment Support |
Attack Types |
Customiz |
Document-ation |
UI/CLI |
Automation Support |
Enterprise Support |
Reporting |
Access Control |
|
Gremlin |
VMs, Containers, Kubernetes |
Resource, State & Network |
No |
Yes |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes (Basic) |
Yes |
|
Harness CE |
Kubernetes, VM Ware, Bare Metal, AWS, Axure, GCP |
Container/pod attacks, VM Ware, Linux, Cloud Compute, Cloud Storage etc. |
Yes - Customizable Resilience Probes |
Yes |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Chaos Blade |
Docker, Cloud VM, Bare-metal |
Resources, Application |
No |
Yes (Only Chinese) |
Only CLI |
Limited |
No |
No |
No |
|
Chaos Mesh |
Kubernetes |
Resources, Network (Limited) |
No |
Yes |
Both |
Limited |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
LitmusChaos |
Kubernetes AWS, Azure, GCP |
Container/pod attacks, Cloud Compute, Cloud Storage etc. |
No |
Yes |
Both |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Azure Chaos Studio |
VM & Kubernetes in Azure and Azure Managed Services like Azure Caches / Cosmos dB etc. |
Resource Starvation (CPU, Memory)/Network |
No |
Yes |
UI |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
AWS FIS |
VM & Kubernetes in AWS and AWS Managed Services like RDS, EBS, etc. |
Resource starvation/ |
Only EKS attacks via Litmus can be customized |
Yes |
UI |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
How to roll out these platforms at an enterprise scale?
With Nagarro's Continuous Resiliency Testing (NCRT) Accelerator!
Powered by: NagarroPlatform(s): LitmusChaos, Gremlin, Harness Chaos Engineering Tool
As you select a chaos engineering tool, you will certainly require expertise to roll it out at an enterprise scale.
At Nagarro, we have built a Continuous Resiliency Testing (CRT) accelerator, based on our proprietary Nagarro Resilience Engineering Framework (NREF), to enable businesses to scale chaos engineering efforts quickly across the enterprise. Through this accelerator which is compatible with all the leading chaos engineering tools such as LitmusChaos, Gremlin, Harness Chaos Engineering Tool, etc., teams can execute resiliency testing in every stage of the development cycle.
Given below is the accelerator’s architecture:
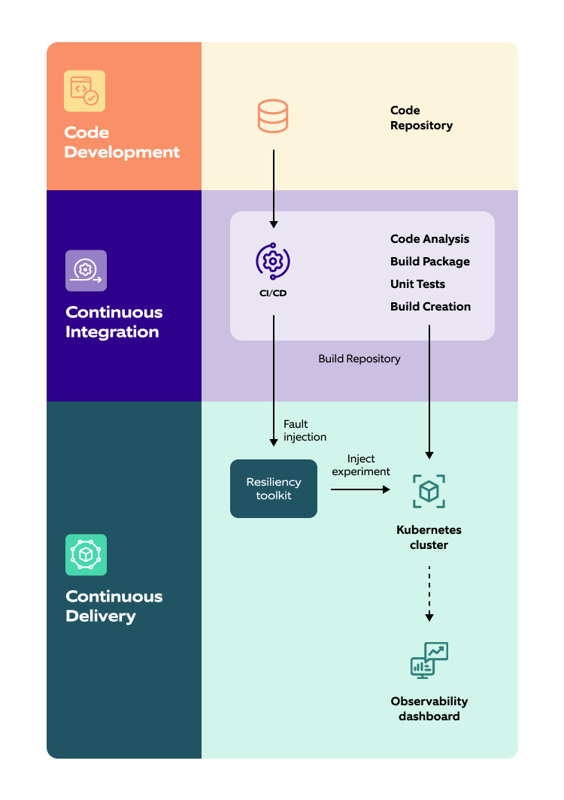
The accelerator can integrate with all the existing platforms (chaos engineering tools, observability, code repository, and others) and enables engineers to automate reliability testing by integrating with CI/CD pipeline. It also makes it easy for teams to design and execute more complex custom tests for specific chaos testing use cases.
Conclusion
Each chaos engineering tool comes with its own pros and cons, based on the environment, attacks, pricing, and so on. Before selecting a chaos engineering tool, one should be focused on what kind of resilience testing is needed within a system. The following approach can be followed to select a specific tool:

Do you require the expertise to help you accelerate your journey to building a resilient software? Get in touch with us today.







