A report by GlobeNewswire states that the global cloud services market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 18% from 2019 to 2027 and cross $1 trillion by 2026. As organizations up their game in the digital transformation and modernization journey, the shift to the cloud over on-premises infrastructure has undoubtedly accelerated.
However, the adoption of cloud brings grave challenges, with the most significant challenge being the management of the spiraling cloud cost. While businesses expect a decline in their capital expenditures (CapEx) and operating expenses (OpEx) with cloud adoption, the reality is very different. Businesses rather start noticing an upward trend in the cost spend and a rise in OpEx, denting their overall budget. (Download this e-book to learn about cloud cost optimization.)
The reason behind this is the cloud’s variable cost model. While in the CapEx operating model, finance and procurement teams have complete visibility on the amount spent on the hardware, cloud adoption transfers the control to engineers and developers. The finance team is excluded from the process, and the engineers and developers get complete liberty of provisioning the resources, resulting in an overall increase in cloud spending. To manage these issues and optimize costs, cloud cost management tools (FinOps tools) can be leveraged by businesses.
What are Cloud FinOps tools?
Based on the principles of FinOps, cloud cost optimization approach brings finance, IT, procurement, and business functions together to create a cost-conscious culture across the organization. It helps enterprises address the complexity of cloud bills and lower the total cost of ownership in different ways such as tagging, cost mapping, right-sizing, removing waste, volume discounts, etc.
FinOps tools are implemented to help cloud teams manage the cloud costs effectively.
While managing cloud costs manually can be difficult, there are several tools available in the market. Whether you are using a single cloud service provider such as Azure, AWS, or GCP, or you run a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud environment, you can leverage these tools to manage cloud cost efficiently.
Why do you need FinOps tools?
Whether you’re trying to curtail rampant cloud spending, increase visibility into cloud spend, purchase a reserved capacity, or drive cultural change across organization to optimize cloud cost, – you must implement a FinOps tool.
FinOps tools' robust features enable organizations to manage hybrid and multi-cloud services and resources, right from providing governance and lifecycle management to automation for managed cloud infrastructure resources.
The tools have been designed to enable organizations manage hybrid and multi-cloud services and resources.
The FinOps tool can either be procured by your organization’s IT team, FinOps team, or a business function and deployed on-premises/in the cloud account or purchased as a SaaS service.
Some of the benefits of using a FinOps tool include:
- Monitoring and fetching valuable insights on cloud infrastructure usage
- Tracking spending and reducing waste through alerts on lowered demand
- Automatically scaling usage to optimal rates
- Identifying areas to cut down the spend by reducing resource usage
- Detecting anomalies/unexpected cost fluctuations by leveraging AI/ML
- Simulating volume discount scenarios or options
- Gaining visibility in container/Kubernetes cost
- Getting recommendations and actionable optimization suggestions
- Enabling auto shutdown of environments/VMs/resources
Read our FinOps 101 blog to better understand why you need FinOps.
How to choose the right FinOps tool?
Native v/s Third-Party Tools
You can select a FinOps tool from a wide array of native and/or third-party tools. But what’s the difference between them?
Native FinOps tools are provided by a cloud service provider and these work only with that cloud. On the other hand, third-party tools support multiple cloud providers and come with features that include: budgeting, forecasting, alerting, policy support, anomaly detection, container costs visibility, and integration with tools like JIRA, ServiceNow (to operationalize the insights, suggestions, etc.).
Features of Native Tools
Native FinOps tools are specifically designed to manage costs within a specific cloud environment. These tools provide the most comprehensive insights and data to help you make informed decisions about your cloud spending. Some of their features include:
- Integration: Native tools are fully integrated with their public cloud service providers, making it easy to manage cloud costs and usage in one place.
- Cost tracking and allocation: Native FinOps tools provide detailed cost-tracking features that allow you to track the cost of your cloud resources in real-time. You can see how much you are spending on different services and where you can optimize your costs.
- Cost allocation: They offer cost allocation features that enable you to allocate the costs of your cloud resources to different departments or teams. This helps you better understand how your cloud resources are being used and who is responsible for their costs.
- Recommendations: Native FinOps tools provide recommendations to optimize your cloud costs based on best practices and usage patterns. This can help you reduce your cloud costs without sacrificing performance or functionality.
Features of Third-party Tools
Third-party tools provide a more comprehensive and customizable solution for managing cloud costs and usage, with support from multiple cloud providers and advanced analytics capabilities. Some of their features include:
- Multi-cloud support: One of the major differentiators between native and third-party tools is that the latter supports multiple cloud service providers, enabling you to manage costs and usage across all the cloud accounts in one place.
- Customizable dashboards: These tools come with customizable dashboards so that you can easily visualize and analyze your cloud spending and usage data as per your business requirements.
- Automation: You can automate tasks such as resource tagging, resource optimization, and cost allocation, freeing up your team to focus on other business-critical tasks.
- Advanced analytics: There is a provision of advanced analytics to help you analyze and optimize cloud usage patterns, identify trends, and predict future costs.
- Cost anomaly detection: FinOps third-party tools use machine learning algorithms to identify cost anomalies and provide recommendations on how to optimize your cloud spending.
What to consider when choosing a FinOps tool?
You need to keep the following factors in mind when choosing a FinOps tool:
Prefer to buy, not build
While developing your own tool that you have full control of may sound enticing, you need substantial time and money. It involves a high level of complexity, effort, development costs, and ongoing maintenance cost. Also, CSPs keep bringing new changes, and you need to keep updating your tool accordingly. Then there is development time involved too, which means that the time to value will be very high. It is recommended that you buy a third-party tool that provides a high level of insights and guidance on reducing cloud bills.
Assess functionality beyond cost optimization
The FinOps tool you select must provide features such as reporting, forecasting, anomaly detection, and active support in a multi-cloud/hybrid environment. If you are leveraging containers/Kubernetes, look out for tools that have the capability to provide insights into container costs too.
A few other points to keep in mind while choosing a FinOps tool include:
- Licensing cost (which may be a concern for organizations with strict budget constraints)
- Level of customization and integration the tool requires to use the external data
- Training requirements to fully utilize the tool’s capabilities
Comparison of leading FinOps tools
Let’s look at some of the cloud cost management tools that can help you generate visibility and help you gain control of your cloud bills.
- Harness
- Apptio Cloudability
- CloudHealth by VMWare
- Spot by NetApp
- Flexera Cloud Management Platform
- Cloud Custodian
1. Harness
Harness is a cloud-native software delivery platform that helps organizations automate and streamline their application delivery workflows across different cloud environments. One of its standalone offerings is the cloud cost management feature that provides visibility into cloud costs and helps your team proactively visualize, manage, and optimize the cloud cost.
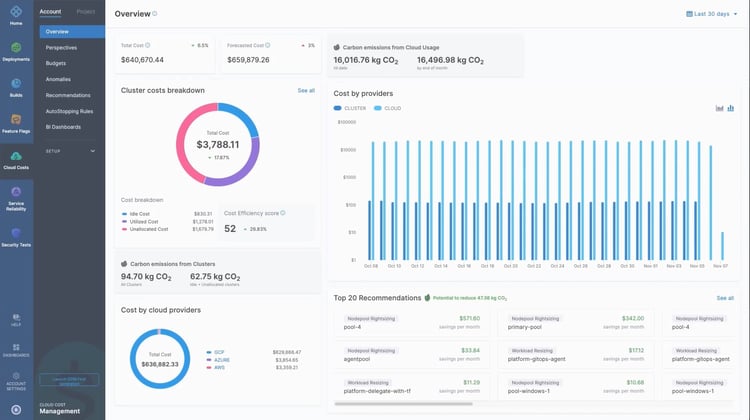 Source: Harness
Source: Harness
Cloud support: AWS, Azure, and GCP
FinOps Certified Platform: Yes
What we like most about the Harness Cloud Cost Management tool:
- Provides relevant information with no tagging requirements
- Provides complete visibility into multi-cloud costs that include container costs
- Provides saving recommendations across workloads
- Offers features such as forecasting, budgeting, anomaly detection, etc.
- Kubernetes/container cost is what sets them apart from the rest
- Connector-based support to turn off/turn on environments when they are not needed saves costs
How Harness can improve:
Since this tool is one of the most popular and effective ones out there, it comes at a cost. People with budget constraints may find it an issue.
2. Apptio Cloudability
Cloudability is a cloud cost management tool that focuses on helping customers get visibility into their spending and manage and optimize it.
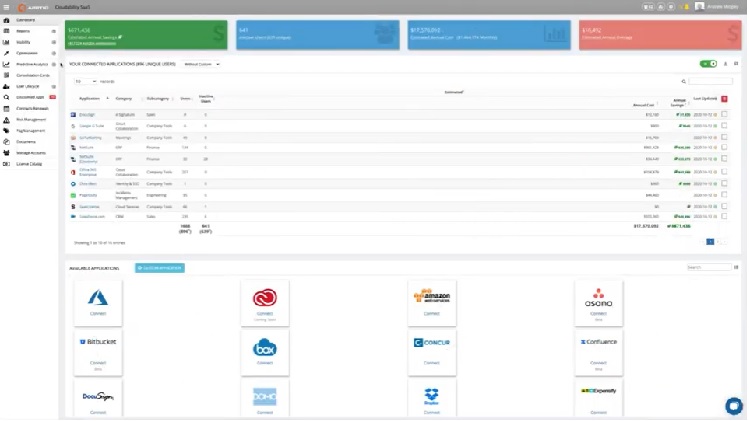
Source: Apptio
Cloud support: AWS, GCP, and Azure
What we like most about Apptio Cloudability:
- Mature tool with an easy-to-use, intuitive interface
- Offers advanced billing and visibility features
- Provides support in resource decommissioning
- Provides cost savings recommendations across workloads, including reserved instance purchasing, and rightsizing
How Apptio Cloudability can improve:
- Doesn’t offer on-premise cost monitoring
- Lacks native support for Kubernetes cost allocation
- Requires manual tagging to get full visibility into cloud spending, including cluster costs such as Kubernetes
- Costs are only visible at a daily granularity
- Can only see changes in cost (these changes cannot be associated to the engineering changes)
3. CloudHealth by VMWare
CloudHealth is a cloud cost management tool that specializes in the governance of cloud costs. It helps create policies that meet compliance and financial management needs.
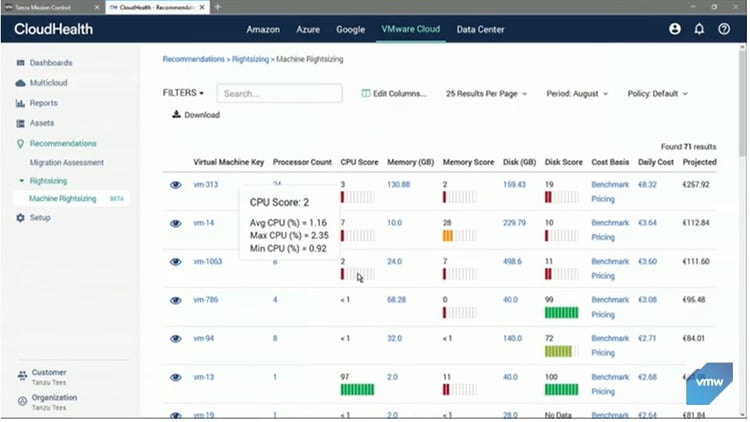 Source: VMware
Source: VMware
Cloud support: AWS, GCP, and Azure
What we like the most about CloudHealth by VMWare:
- Highly configurable as per customer's needs
- Offers governance features to create and manage financial controls
- Can correlate cloud deployments with security risks
- Offers cost-saving recommendations, budgeting, and forecasting features
How CloudHealth by VMWare can improve:
- Doesn’t provide users with details on Automated Idle Resource Management, Spot Orchestration, Cluster Orchestration on Spot Instances, and Automated RI/SP Contract Execution
- Requires good tagging practices to get full visibility into cloud spending
- Difficult to create multi-dimensional reports
- Doesn’t provide full audit trails
4. Spot by NetApp
Spot is a cloud cost management tool that focuses on helping businesses automate their cloud cost optimizations based on data. It provides a suite of features for cost optimization, workload automation, and infrastructure scaling for public cloud providers.
Cloud support: AWS, GCP, and Azure
What we like most about Spot by NetApp:
- Provides automation capabilities to optimize cloud infrastructure
- Offers recommendations for optimization
- Provides cost trends as per usage patterns
How Spot by NetApp can improve:
- Requires good tag management
- Users can only see changes in cost
5. Flexera Cloud Management Platform – Optima
Flexera Cloud Management Platform (CMP) is a comprehensive cloud management tool designed to help organizations manage and optimize their cloud resources across multiple clouds and accounts. Optima is a key component of the CMP, providing a suite of cost management and optimization capabilities for public cloud providers.
Cloud support: Azure, AWS, and GCP
What we like most about Flexera Cloud Management Platform – Optima:
- Provides a unified view of cloud resources, making it easy for organizations to monitor and manage the environment
- Provides details documentation which makes it easy to use
- Integrates easily with cloud billing and usage reports
How Optima can improve:
- Doesn’t offer on-prem cost monitoring
- Lacks support for Kubernetes or spot instance orchestration
- Its cost anomaly alerts feature is a static reporting module that requires manual configuration to receive alerts
- Lacks several functionalities across the three-cloud service providers
- Lacks advanced visibility features
6. Cloud Custodian
Cloud Custodian is an open-source and CNCF Incubating Project under the Apache 2.0 license. The tool provides a flexible and scalable way to manage AWS, Azure, or GCP cloud infrastructure resources through automated policies. It can help enforce compliance, manage costs, and improve security across the cloud environment.
Cloud support: AWS, Azure, and GCP
What we like most about Cloud Custodian:
- It's an open source; thus, free to use, and you can build your own solution on top of it
- Enables accurate cost tracking and analysis by ensuring that the resources are properly tagged with cost allocation tags
- Helps identify underutilized or idle resources and take action to terminate or resize them
- Helps monitor data transfer costs between regions, accounts, and services and helps you take appropriate action to reduce them
- Helps set and enforce budget limits for individual accounts, services, or entire organizations
How Cloud Custodian can improve:
- Requires technical expertise and familiarity with YAML or JSON syntax to define policies. This means a team or resource is always maintaining the solution built on top of it.
- Doesn’t provide a lot of flexibility and customization to the users. It all depends on how much you can develop on top of it as your own custom solution
- It is complex to set up and maintain and requires careful planning and testing to ensure that policies are working as expected
With a well-crafted strategy, you can also align accountability to cloud users and build confidence around budgets and forecasts. These FinOps best practices will help you implement it by using industry-leading methods.
Our recommendation
While several FinOps tools are available for teams to use, the one you select depends on your requirements. In case you are using mono-cloud, you can leverage the FinOps tool native to that specific cloud provider to get valuable insights and make decisions to optimize cloud usage and costs. While they may provide basic functionality, a matured solution is recommended if you require advanced dashboarding/automation of solutions.
However, for multi-cloud users as well as those heavily using containers like Kubernetes, we recommend evaluating third-party tools that offer a myriad of features and functionalities that suit your business requirements.
There could also be a scenario where you may be using one of the above-listed third-party tools. If the tool can seamlessly integrate with your cloud platform and provide effective cloud cost management, we recommend you leverage their offering. For instance, if you are already using Harness (which offers a wide array of tools to support Software Development Lifecycle, including chaos engineering), you can use the Harness cloud cost management module instead of buying another tool. This will save you time and effort in evaluating another standalone tool for this service.
As you advance in your cloud modernization journey, the implementation of an appropriate tool can help simplify cloud cost optimization at any level. Power up your cloud strategy with Nagarro's Cloud Pulse, our proprietary multi-cloud governance platform and ensure your cloud environment stays cost-efficient while delivering optimal performance, reliability, and enhanced security. With our team of FinOps experts, we can help you choose the right cloud cost management and optimization tool as well as implement it across your organization.