Knowing the customer is pivotal for every industry, such as banking, aviation, automobile, manufacturing or e-commerce. Sending personalized offers, maintaining relationships, and addressing customer needs are essential for the success of any business. A business that knows its customers and their end-to-end journey with it, is much more likely to maintain long-standing relationships with its customers.
What is Customer 360?
Customer 360 denotes a 360-degree or a complete view of your customer. This approach provides various insights to businesses so that they can:
- know the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
- find the most valuable customers to retain
- deliver personalized offers
- know the best way to contact customers
- retain any customers whose interest/engagement is waning
- increase revenue/growth
The idea behind the Customer 360 solution is to provide a single view of the customer with data from different sources and use it for maximum business growth.
What are the key challenges?
To grow rapidly, every business should understand its customers better. Businesses face the following challenges in creating a Customer 360 view:
- Multiple data sources: Data generated from different sources like website, marketing, social media, customer care, etc.
- Overlapping and conflicting information: Certain data sources contain overlapping/same and conflicting/different information as it is collected via different channels.
- Semi/Unstructured data like call center records, voice calls, images, videos, etc.
- Real-time streaming data like sensor data.
- A large amount of social media data from Facebook, Twitter, etc.
- Data volume: The amount of data generated is huge and is growing day by day.
Sample customer profile:
A sample customer profile includes complete information about the customer such as demographic data, purchase history, relationship with business, etc. Customer 360 view can be understood as a crystal ball, where one can see the customer’s past, present, and predicted future with the brand.

Sample Customer Profile
Flow diagram:
Customer 360 view consists of data from multiple sources, which keeps getting updated as new data flows into the system. Advanced analytics is run on the central repository of customer data to generate insights, which help in getting to know the customer better from a business perspective. A sample flow for creating and leveraging the benefits of Customer 360 looks like this:
 Customer 360 – Flow Diagram
Customer 360 – Flow Diagram
- Data sources: The first step is to define all the data sources of customer information - structured (CSV files, relational databases, etc.), semi-structured (JSON files, log files, etc.) or unstructured (images, videos, etc.). The data can either be batch data - available for one-time processing, or streaming data - which keeps flowing into the system in real-time.
- Update data: As new data flows into the system, it is essential to update the data under the centralized data repository periodically. Big data processing tools are used to create a centralized repository. This repository contains data from different sources - cleaned (by removing the garbage values) and joined (by merging the data from different sources).
- Customer database: By using big data processing and advanced analytics, the data is processed, and a unique customer database is created, as per the defined business rules. This database is updated as new data comes into the system. The customer 360 database consists of all the customer-related information that is processed, to leverage its benefits.
Marketing and sales teams use the Customer 360 database to optimize their campaigns. For example, the teams use this data to send personalized offers to customers. Customers are further segregated as per different parameters like age, region, location, occupation, lifetime value, churn predication value, etc. The response from these campaigns is also used as a data source and is further processed to generate various insights in future.
The following diagram shows the different layers through which data is processed to create the Customer 360 database. It also displays the different technologies that can be used to leverage the benefits from this database.
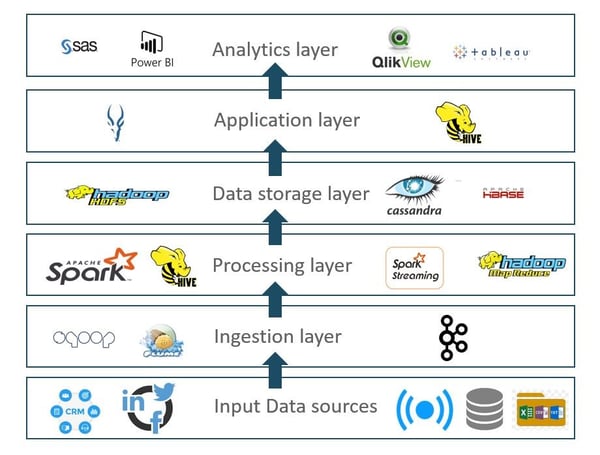
Customer 360 – Different Processing Layers
RFM (Recency, Frequency, Monetary) Score:
RFM is the industry standard term to know the value of a customer. RFM is used to calculate how a recent customer has transacted with the organization – displaying the topicality (how recent), frequency, and the monetary value of these transactions.
Divide the customers into different categories for each metric (recency, frequency, and monetary) based on the distribution of metrics. Based on these metrics, every customer is assigned an R score, an F score, and an M score - between 0 to 10.
The RFM score is calculated by combining all these values.
The higher the RFM score (R score, F score, or M score), the better (prospect) the customer is for marketing (efforts).
After calculating the RFM score, one can query the database to sort those customers who belong to a specific marketing campaign requirement.
For example, one can say, I want customers with a score above 16 RFM but who should also have an F-score of more than 6. The data used for different marketing campaigns is based on the RFM score.
The possible use cases from RFM scores are as follows:
- Possible churners (customers having very low R score and F score) are customers who have not returned for more than two years and have a low chance of coming back; Focus on the ways to stop customer churning.
- Focus on the potential performers (Good RFM score and have recently joined) because they can sway towards either side, if not nurtured well.
- Plan and optimize the suggested campaigns – Bring-them-back campaign and retention campaign.
Customer Segmentation:
As per their parameters, customers are categorized into either micro or macro segments. These segments can be derived on various like age, location, spending history, channel preference, content preference, social influence, churn score, usage patterns, data usage, RFM score, language, etc.
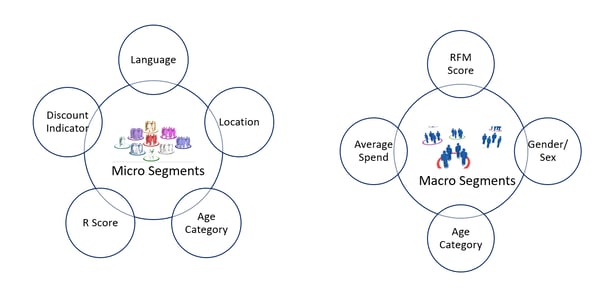 Customer Segmentation
Customer Segmentation
Marketing campaigns are run for the targeted audience as per these . Personalized campaigns can be run based on micro-segments.
Use cases of Customer 360:
- Targeted marketing and personalization: Customer 360 enables us to treat customers as per the information gathered after collating and analyzing their data. This data forms the basis for the personalized offers and discounts that are sent to customers.
- Customer retention/Churn prevention: Customer 360 helps businesses to retain their customers. If a customer has not transacted with the business in the recent past, specific offers can be sent to that customer.
- Proactive customer care: Customer 360 can be used to take care of your customers proactively. Whenever any customer’s experience index falls, an alert can be generated, and customer care can connect directly with the customer to provide an appropriate resolution.
- A holistic view of customers: Customer 360 provides complete information about a customer in a single view.
- Know customer lifetime value: Customer 360 helps us to identify the customer lifetime values, which can help in ascertaining the most valuable customers.
- Loyalty programs: Customer 360 helps in running loyalty programs for the most loyal customers so that they do not sway towards other vendors.
Implementing Customer 360 helps us to understand our customers better so that we can take care of them proactively. It helps maintain a long-standing relationship with them. Nagarro helps its customers in drawing a roadmap for implementing Customer 360 and identifying various use cases for their business.




