The constant evolution of the banking industry has developed many new financial sectors. One of them is Islamic banking, which is among the fastest-growing segments in today's banking landscape.
Islamic banking offers an alternate system of banking practices in pre-dominantly Islamic economies. Though it provides Muslims with a different banking system, it is not limited to only Muslims. Let's us now understand Islamic banking, its evolution, business models, and how it has found its feet in the financial markets.
What is Islamic banking?
Islamic financial system offers most of the banking and finance services similar to conventional banking with a few key differences. Islamic financial activities adhere to the principles of Sharia law, which are known as Fiqh al-Muamalat (the jurisprudence of transactions). The tenets that govern all commercial transactions like borrowing, lending, and investing money are derived from the teachings of the Quran, the most crucial religious scripture in Islam.
As with other types of banking, the Islamic financial system's practices base themselves on the moral principles of finding a responsible way to conduct banking. Islam does not consider money to have any intrinsic value. It's a means to serve social or spiritual purposes, and therefore, cannot be owned by any single entity.
These are the core fundamental principles in Islamic banking:
- There should not be any usury or interest charged (riba) on any money that is lent.
- All commercial transactions should be conducted such that any profit, loss, or risk is shared between the involved parties.
- Any speculative activities or games of chances as defined in the Sharia should not be financed.
- No investments should be made into any businesses or activities that are forbidden in Islam.
Islamic banking promotes an interest-free economic structure based on cooperation and equal participation between the bank and the customers, who are expected to abide by Sharia rules. In case of any doubt regarding the code of conduct, they may consult learned scholars for more guidance.
Islamic banking is still in its nascent stages, with only about 2% of all assets worldwide being held with Sharia-compliant financial institutions. That is approximately USD 2.88 trillion, as of 2019. The rules of conducting business as per Shariat are still evolving to keep pace with the changing times and sometimes vary in different countries. The Islamic Financial Services Board (IFSB)* has been set up as a governance body to promote stability and transparency, and provide a unified structure for Sharia-compliant finance by issuing global standards for Islamic banking.
*One of the two major Islamic financial regulatory bodies, the other one being Accounting and Auditing Organisation for Islamic Financial Institutions (AAOIFI)
How did Islamic banking evolve?
Since medieval times, Islamic banking has been in practice, but the earliest example of a modern-day successful Islamic financial institution comes from Malaysia-based Tabung Haji. It was founded in 1963 and offered interest-free money to Muslims to help them make their Haj pilgrimage. This setup was not possible within the western banks operating in Malaysia because regular banks offer loans with a different paradigm. The institution saw manifold growth quickly and made a case for more banks to be established under the Shariat.
With the influx of petrodollars in the Middle East, Islamic banking and finance industry began to pick up in the 1970s and has seen a noticeable expansion across most of the Arab world with its Muslim-majority population and growing economies.
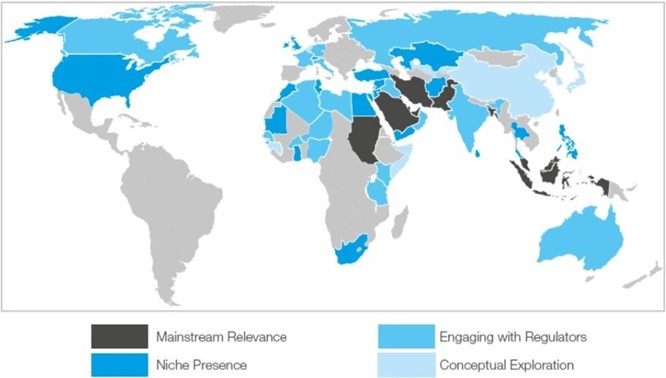 Figure 1: Presence of Islamic Banking – Worldwide [Image Credit: KFH research]
Figure 1: Presence of Islamic Banking – Worldwide [Image Credit: KFH research]
Here are some interesting facts about Islamic banking:
- The MENA region (the Middle East and North Africa) is home to more than 200 Islamic banks.
- With a 25% share of the Islamic finance ecosystem, the Asia Pacific region is close second, and promises further growth.
- Islamic banking has a marked presence in over 100 countries across the globe and has seen a consistent growth rate of 10-13% year-on-year since the early 2000s.
- As of 2020, there are approximately 520 banks and 1700 mutual funds around the world that comply with Sharia principles.
- Over the last decade, Islamic banks' capital holding increased from USD 1.5 trillion to 2.8 trillion. Given this exponential growth rate, this amount is expected to cross USD 3.6 trillion by the end of 2024.
.png?width=2250&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(21).png) Figure 2. Global Islamic Finance Assets (USD Trillion)
Figure 2. Global Islamic Finance Assets (USD Trillion)
What are the business models for Islamic banking?
Islamic banking has matured to set up different business models across the globe, as per the applicable region. Often, the catalyst behind such setups is the parent conventional bank's strategy to tap into a budding market and provide additional financial services for their segmented customers.
In such an ecosystem, an Islamic financial institution can be any of the following:
- a full-fledged standalone Sharia-compliant bank
- an Islamic window - these are separate Sharia-compliant units within conventional banks, offering Islamic investment products
- an Islamic subsidiary of another conventional bank
- or an NBFC that follows Islamic banking practices
Islamic windows are an interesting concept because they sit within conventional banks which offer regular run-of-the-mill financial services and products while also catering to a target customer base that wants to invest in Sharia-compliant instruments. Many successful global banks like HSBC, American Express, Chase Manhattan, UBS, BNP-Paribas, etc. have adopted this business model.
Citibank, UBS, and Bank Negara (Malaysia) also have operational Islamic subsidy banks. As per current trends, with time, the Islamic windows are expected to transform into independent subsidiary banks.
NBFCs that adhere to Islamic principles are gaining traction in regions and countries where an alternative banking methodology does not fit. In these cases, NBFCs can offer financial services for the marginalized customer base that prefers Sharia-compliant banking and investments.
Fintechs and Islamic banking - what does the future hold?
Financial technology (fintech) is the name of the game for the BFSI sector. Several banking-related innovative and disruptive ideas when successfully implemented have transformed BFSI business models across the globe. Islamic banking is also adopting fintech to:
- streamline their business processes
- widen the reach of their products
- engage more customers
- generate added revenue
- provide an overall better banking and investment experience.
As of 2020, as many as 1.9 billion people actively use online banking and financial services. This number is poised to reach 2.5 billion worldwide by 2024. Clearly, digitalization is not just a good-to-have option anymore but more of a must-have mandate for any bank to thrive. The Islamic community's increased affluence and spending power means that banking practices and products also need to evolve continuously. The Islamic banking software market is expected to grow by USD 461.83 million during 2020-2024, progressing at a CAGR of over 13% during the period.
As per the Global Islamic Banker's Survey (GIBS) 2020 report:
.png?width=2250&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(22).png)
How are Islamic financial institutions leveraging technology?
Many established software companies have emerged as leading market players, offering Islamic banking software according to Sharia norms. This includes the distinctive features that define Islamic banking and these vendors' contracts and agreements with their clients. The out-of-the-box software solutions developed by these vendors offer full-spectrum support for Islamic products and associated services. They implement the salient principles of
- Murabaha (cost-plus)
- Mudarabah (profit-sharing and loss-bearing)
- Musharaka (joint ventures)
- Ijarah (leasing)
- Istisna (construction-related business)
- Salam (payments)
The solutions incorporate the Hijri calendar, offer multi-language support, and are configurable to meet local compliance and market needs.
Most Islamic financial institutions are also seeking scalable, robust, and secure solutions that leverage the latest technologies like cloud, big data, blockchain, etc. with 360-degree customer view, enhanced KYC (especially after the Covid pandemic), open banking, and a platform for the banks to innovate with new Islamic products (in line with Sharia rules). Digital and social banking solutions that allow easy access and a unified customer experience across channels are already recognized as game-changers for Islamic finance.
Long story short
In 1999, when Dow Jones established its Islamic Market Index for investors interested in Shariat-compliant projects, it indicated the development of a new banking segment. Today, the US has a Sharia-compliant financing house called LARIBA. In contrast, the UK (a non-Islamic country) has, a first, established its Islamic bank and issued Islamic bonds in its financial markets.
Many countries like China, Australia, Germany, Luxembourg, and Switzerland have ventured into the Islamic financial ecosystem by opening Islamic windows or introducing Sharia-compliant funds and bonds. Islamic banking is also taking roots in sub-Saharan Africa and South America.
Islamic banking has already developed a global appeal due to its transparent, safer, asset-backed financing, interest-free offerings, and expanding customer demand. It seems like an exciting point in the evolution journey of a niche banking segment, which is at the precipice of growth.
Nagarro is working in this segment, especially in the Middle East. As part of our specialty advisory services, we are augmenting core banking services for a leading retail and corporate financial group. Nagarro is their preferred strategic and digital transformation partners. For another major banking client, our digital solutions team created a lifestyle banking app for millennials that supports both conventional and Islamic banking customers. Our service offerings also cover legacy system modernization, fintech and digital solutions, agile transformation and coaching, design and user experience workshops and enterprise architecture consulting. Want to know more? Explore our offerings and connect with our experts!





