Knowledge management ensures that the right information is delivered to the appropriate place or person at the right time. It enables organizations to improve the quality of management decision-making by ensuring that reliable and secure information and data is available throughout the service lifecycle.
Knowledge management is of critical importance to service providers, because unlike earlier, it now allows them to sell knowledge much more comprehensively. This has been made possible through well-defined processes, best practices, tools, and increased specialization, and most importantly through increased focus on service knowledge management system.
Most of the frameworks and guidelines for knowledge management (like ITIL, CMMI, and ISO 9000), primarily focus on:
- Converting ideas and concepts into services for customers with increased capability
- Solving problems effectively with pertinent solutions, leading to improved service quality
- Controlling the cost and risk
- Learning from success and failures to manage challenges and create opportunities
- Durability, portability, and broader reach of the knowledge assets
Knowledge assets contain technical knowledge as well as process, domain, operational, and regulatory knowledge.
Knowledge management is an important factor while designing the services to be offered. Various artefacts like plans, process, templates, tools, and roles are defined while designing a service offering. These can be customized as per the needs of the services during the service transition.
1. Service transition- Knowledge transfer process
Knowledge Transfer (KT) is a key activity in any service transition plan- for a new service or a change in service. New services can begin only after the required knowledge transfer process has been completed.
1.1 Entry criteria
Knowledge transfer starts as soon as the customer is engaged during the service design phase, but a comprehensive plan and formal commencement of knowledge transfer starts with the service transfer phase.
1.2 Input
The following table describes various inputs and mechanisms for knowledge transfer:
|
Categories |
Common knowledge transfer mechanisms |
|
Technical knowledge (system design, design rationale, how the code is organized, code documentation, and code) |
|
|
Administrative knowledge (deployment model, network topology, hardware environment, software stack, customizations, configurations, backups) |
|
|
Functional knowledge (how end-users use the site, roles, profiles, process flows, etc.) |
|
Inputs and Mechanisms
1.3 Process
Service transition manager creates the knowledge transfer strategy in line with the needs of the service to be transferred. An effective knowledge transfer strategy should address the following key areas:
- Creating a governance model
- Establishing roles and responsibilities
- Finding policies, processes, procedures, and methods for knowledge transfer
- Identifying expertise and knowledge required to deliver a service effectively
- Finding technological, administrative, and functional knowledge transfer requirements
- Determining KPIs
Nagarro has many process documents, templates, and checklists which are used by service transition manager to establish a KT strategy.
Based on the KT strategy, an appropriate KT plan is created. A knowledge transition plan contains the following:
- List of documents (user manuals, deployment guides, ready reckoner for incidents, technical documents, process documents)
- Target completion date
- Plans for instructor-led training, web sessions, and any other training document (presentations, videos), if required
- Details of the knowledge management tool (like SharePoint), and artefacts (repository/tool location, access, intended audience)
After sign-off, the knowledge transition plan is executed and tracked.
Regular feedback is a necessary part of tracking the plan and necessary changes are made to the plan, training material and methodology.
Nagarro has developed templates and checklists to help in creating a knowledge transition plan, capturing the training requirements, and assessing the effectiveness of the trainings. Reverse knowledge transfer sessions/quizzes/tests which assess the efficacy of the activities, are a critical component of a robust knowledge transition plan.
Knowledge Management Plan:
Build the plan-
- Application service assessment
- Business specific application assessment
- Skills capability matrix
- Technical specification assessment
- External factors assessment
Execute the plan-
- Assessment of acceptance criteria
- Knowledge management transfer process
Maintain the plan-
- Change requirement
- Business change
- Resource development
- Process changes
- Knowledge Transfer (KT) implementation status
Establishing a knowledge management system is a key milestone. The knowledge gained during KT and through continuous learning should be stored in a well-established knowledge management system.
1.4 Deliverables
The key deliverables of the knowledge transfer phase include:
- Knowledge transfer plan
- Knowledge management system
- Training documentation
- Known Error Database (KEDB)
1.5 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Schedule variance & effort variance
- Number of artefacts created
- Time spent by a customer
- Time spent in documentation
- The number of escalations required during transition
- Successful implementation of the early phase of operation
2. Continuous knowledge management
During service operations, an effective service knowledge management system allows managers to make better decisions, improve service availability, optimize capacity utilization, and fix problems. It is imperative that the process of gaining knowledge should not stop while moving from service transition to operations. It is the responsibility of the service manager to ensure a seamless transition.
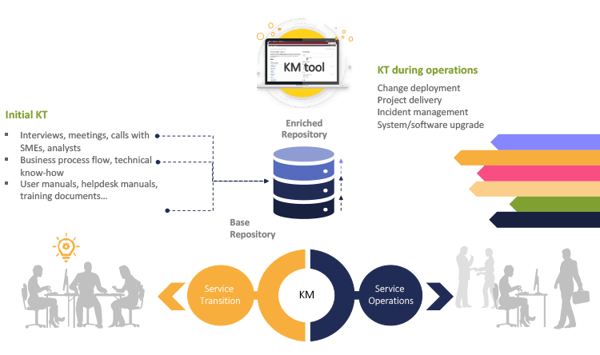
Service Knowledge Management Process
A continuous maturity process can be achieved by following the steps listed below:
- Maintain a healthy relationship with the vendors
- Put a proper knowledge management system in place
- Provide end-to-end training to the client-facing resources
- Implement cutting-edge analytics to understand and predict the issues
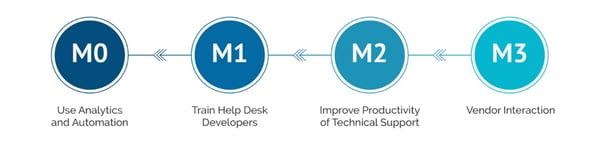 Maturity Model
Maturity Model
2.1 Inputs
- Incident management
- Problem management
- Knowledge transfer plan
- KEDB
- Organizational inputs
2.2 Process
The Service manager is responsible for creating a service knowledge management system and plan according to the needs of the service. The primary objectives of this plan are:
- Establishing the process of collecting data
- Defining plan for the induction of new resources and for the training needs of the team
- Establishing KPIs for knowledge management
- Determining goals for service improvement and tools for tracking
- Reducing risks of availability and service quality
- Managing incidents and problems proactively
The service manager has various templates, checklists, techniques, and knowledge management database of the organization to help in creating a service knowledge management system and plan. This plan is shared with stakeholders for review and sign-off. After approval, the plan is executed and tracked.
The service manager is also responsible for defining different types of access to all the artefacts. These are categorized into 4 roles: Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed.
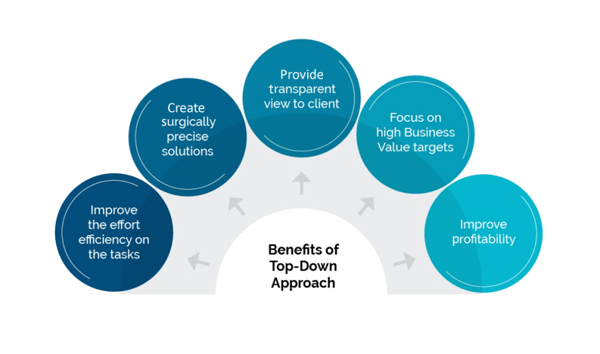
ResultsThe knowledge management process helps in analyzing the efforts put in towards development, maintenance, and support. This helps in identifying the scope of improvement required to achieve higher efficiency and productivity, thus improving project profitability. A top-down approach enables the team to improve the effort spent on the tasks surgically, giving the client a transparent view of the ongoing processes. Such a surgical approach will help the team to achieve the yearly targets by identifying and focusing on the high business value activities.
2.3 Deliverables
- SLAs
- Metrics
- Knowledge management plan
- Induction plan
- Resource capability/maturity plan
- Training gap plan
- KEDB
- Service improvement plan
- Documents like operational manuals, ready reckoner
2.4 KPIs
- Improvement in SLAs
- The ability to solve issues directly without external support
- Decrease in issues falling in the category of “Lack of Knowledge”
- Improved incident and problem management
- Increase in the skill and capacity of the team
3.Templates, checklists, and tools
A well-established knowledge management tool and repository is necessary to effectively execute a knowledge transfer plan and knowledge management plan. Tools and repository should be identified at the time of service design. The methodology of how we use these tools can mature during service transition and operations.
Knowledge Management Plan
Many tools are available to fulfill the key objectives of a knowledge management tool. These objectives are:
- Ease of storing and retrieval of data and knowledge
- Flexibility of integration with incident/task management tools
- Ensuring durability of the knowledge assets
- Offering robust access management, ensuring the correct person gets the relevant information in a timely manner
Various artefacts like plans, templates, training materials, checklists are stored within the knowledge management tool. Location and access information of these artefacts are defined in the knowledge management plan.
Nagarro recommends SharePoint as the knowledge management tool. We also have a team with high capability in installation and usage of various incident management tools like JIRA, Remedy, and platforms like ServiceNow. However, we also have the flexibility of using tools recommended by our clients.
SharePoint has various features like document repository, Wiki, task management module, apart from this, its easy integration with the project management tools like Microsoft Project makes it a gold standard among other knowledge management tools.
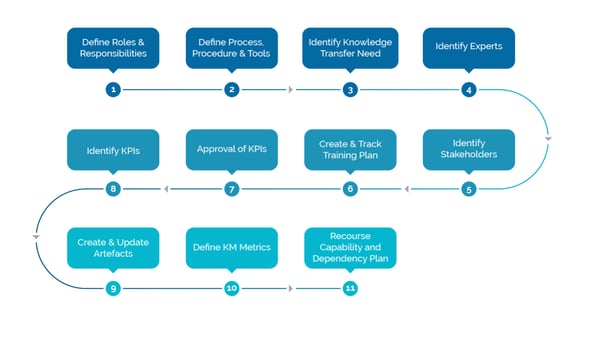
A service manager needs to create/maintain/refer various plans, checklists, and templates to ensure effective service knowledge management, including:
 Knowledge Management Steps
Knowledge Management Steps
3.1 Skill module and training
To understand the depth and breadth of the knowledge of resources at a granular level, one needs to create a Skill Module Dependency Matrix. The resources can score themselves as per their knowledge in every project module and on their technical expertise in tools and technologies. The rating will be validated and verified again by a senior member to ensure the credibility of the score.
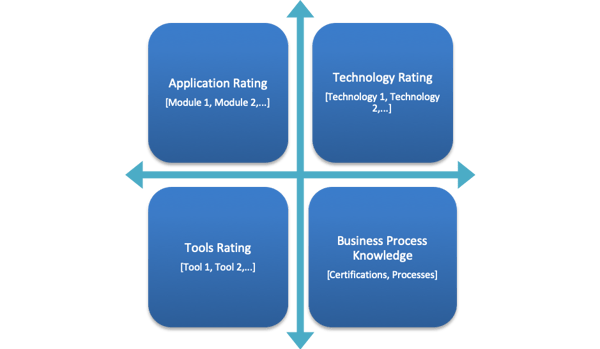
Skill Module Matrix
The resources must be upskilled and cross-skilled regularly to ensure that they stay abreast with the changing IT world. Besides this, fresh resources must be inducted to maintain an effective knowledge flow within the team. A training plan must be devised to ensure continuous improvement in expertise of the resources.
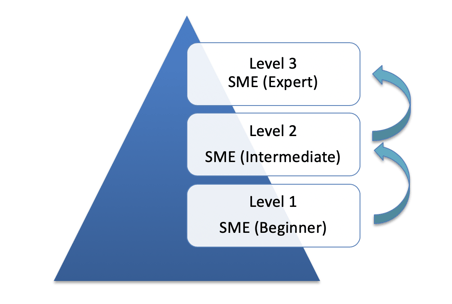 Training & Scoring Model
Training & Scoring Model
This can be achieved by an SME (Subject Matter Expert) scoring criteria, where the resources are trained to reach the highest level and new resources are inducted on a periodic basis for risk mitigation and to maintain a healthy knowledge balance.





