Innovations are an important success factor for companies. But before a business idea reaches the market, it must overcome any hurdles regarding its technical feasibility and commercial success. This is where the proof-of-concept (PoC) comes into play, serving as a tool for analysis, testing, and decision-making. In this paper, the PoC is presented as a method to verify the feasibility of business ideas and to minimize technological uncertainties.
Ideas at the start
Do you know this? An innovation management tool, ideation process or design thinking workshop can generate ideas with the involvement of many motivated employees. These are examined from different angles, checked for possible customer needs, found to be in line with the corporate strategy and selected by stakeholders. Once all these fundamental ingredients are ensured, it's there: the business idea.
The immediate question afterwards is this: Is the idea even feasible for us? For innovators, this seems like a sudden "step back", out of the "flow of cool ideas". But it's not procrastination, it's an important question at the right time. The implementation of ideas is fraught with many uncertainties and risks for companies, and these must be cleared out of the way as early as possible in the innovation process.
Hurdles to overcome
New ideas often arise from a "technology push". The use of a new technology-based product or service appears promising, the market potential is often still unknown, and the need must first be evaluated. In contrast, "market-pull" ideas arise from knowledge of customer and market needs. Technological implementation initially remains a question mark - but there is no getting around it. In today's predominantly digitally-driven innovations, almost every business idea has to face the technology question. You quickly realize: The answer is complex and requires clear decisions:
- Technology selection: The technology must fit the requirements of the company and the innovation. We must also ensure to consider technical as well as functional aspects, along with the required resources. Different technology providers and solutions must be compared and evaluated; in the B2B area, they must often be brought in line with the existing customer systems.
- Future viability: To ensure that the technology remains usable in the long term, it should be selected for future needs, adapted to new systems and developed continuously. It should also have sufficient support and know-how.
- Scalability: If the innovation project is successful, it should be possible to easily scale and expand the technology to handle increased usage.
No straight path to the goal
Uncertainty and risk in technology-based innovation are increasingly rising. The use of cloud platforms and artificial intelligence applications is continuously increasing since they determine the competitiveness of companies. The most important question remains, "Which horse should I bet on?"
To answer this question, you must consider the following aspects:
- Integration with or replacement of existing systems: An important aspect of introducing new cloud-based technologies and AI applications is integration with existing systems. Many companies have a complex IT infrastructure and the integration of new technologies can lead to compatibility problems or significant new investments.
- Regulations, security and data protection: Regulations (such as DSGVO, Digital Service Act or future EU AI Act) - that define the use of data based on legal and ethical principles - set new frameworks for the use of digital technologies. Companies need to ensure that their data is safe and secure, especially when it comes to sensitive information such as customer data, business information or intellectual property.
- External customer requirements: When PaaS/SaaS solutions are deployed, internal company systems and processes are often opened up for the first time. Here, it is important to ensure that the technology can be integrated flawlessly into the customer's existing business processes and that the requirements regarding security, data protection and compliance are fulfilled adequately.
Technological uncertainties are another big obstacle in implementing new business ideas. An idea might look promising on paper, but technological challenges can make it difficult to realize. Many business ideas reach their limits here. As a result, some give up at this hurdle, others decide to "close their eyes and go for it" (often getting disqualified in the end); those who are really successful are those who calculate and target the run-up to the big jump.
The targeted approach: "Proof-of-Concept"
Proof-of-concept (PoC) enables companies to evaluate the feasibility of business ideas, identify potential problems early on, and solve the biggest issues before actual implementation.
At Nagarro, we have developed a PoC methodology that is iterative, tech-founded, and partnership-based. All our experience from client projects around the globe has gone into this PoC methodology, which has now proven excellent in supporting innovation processes and implementing new technologies for companies across a wide range of industries. It has been shown that external experts can contribute valuable experience for the PoC from other projects and industries. They approach the business idea without bias, are better able to assess technological uncertainties and market risks, and make recommendations because they are not affected by internal "operational blindness".
That’s not all. Here are some more benefits of having external experts
- Expertise: These experts have deep market insights and a sound understanding of different technologies and their application in different industries. They can evaluate the adaptation and implementation effort based on experience and can better assess future viability.
- Objectivity: Due to their independence, they can offer an objective perspective and valuable insights into the different technological options on the market.
- Resources: They provide additional resources and support, such as specialized software tools for test applications.
- Expert pool: They can access their pool of subject matter experts for detailed questions and have a wide network of partners to help with PoC decision-making.
- Effectiveness: They increase the effectiveness of the PoC by relying on tried and tested methods, tools, and proven processes.
Nagarro’s PoC Methodology: The stage goals
Our PoC method is divided into four stages. We start with analysis before moving into two iterative stages: Based on the design, exploration takes place. The results have an immediate impact on the design. The ongoing repetition of this control loop means that different perspectives and requirements (internal test group, selected customers, different technologies, etc.) are already incorporated in the PoC phase. In addition, work is done on selected pilots, show cases, MVPs, etc., so that the evaluation of the idea can be as practical as possible. Ultimately, this allows concrete recommendations for action to be derived.
Let's take a look at the four phases in detail: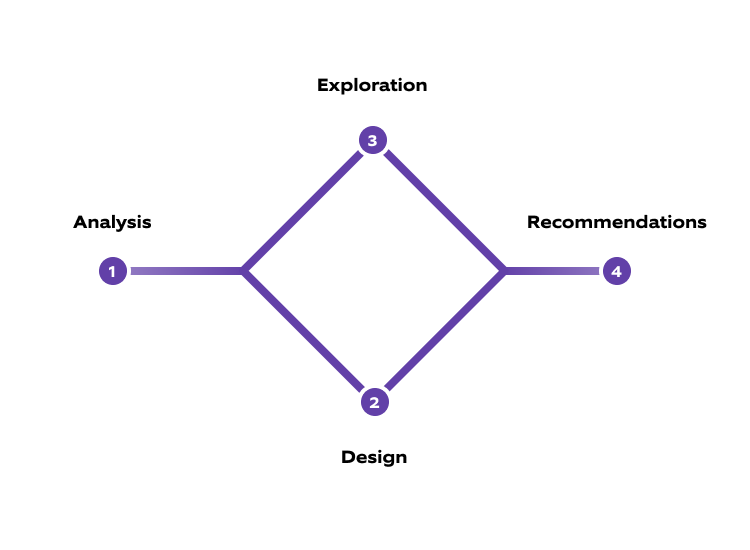
- Analysis: The scope and requirements for the PoC are defined. One focus is the analysis of the technical feasibility and economic viability of the idea. Among other things, questions about cost-benefit efficiency and technological challenges are answered: What solution is being targeted? What is already available in the market? What is suitable for the company and, if applicable, its customer network? Research, market, technology, and system analysis are carried out and the results are processed accordingly.
- Design: The design for the implementation of the business idea is defined as well as for the first application in individual areas (pilot, MVP, etc.) including requirements and decisions about resources are made. [Iteration with phase 3]
- Exploration: This phase involves creation or implementation and testing of the pilot, MVP etc., which will be used for specific employees or customers: here, a wide range of usage insights (user acceptance, IT system performance etc.) are to be gained quickly. In parallel, testing and adaptation is performed and it is ensured that the right outcome is produced. Iteratively, conclusions are drawn about the design and it is adapted accordingly. [Iteration with phase 2]
- Recommendation: The recommendation serves as a well-founded decision of the company on the business idea, based on research on technological and market-driven implementation possibilities including already incorporated practical feedback. This can be supplemented by an outlook on further potential use cases or the outlining of a strategic (technology) roadmap.
The successful hurdle jump
Today, innovation in companies is characterized by uncertainty and insecurity. Be it for markets, customer requirements or new technologies, for the generation and evaluation of business ideas, this means you have to become quicker and more flexible to be able to react to changes in the framework conditions in a customer-oriented manner. Companies must create conditions that help them develop new, innovative business ideas that enable "decidable decision-making" despite uncertainty and insecurity.
A PoC is a helpful method to help test the feasibility and effectiveness of a new idea or technology and reduce uncertainty. Nagarro extends the classic PoC to include "practicality" and an iterative process, i.e. with tested pilots, showcases or minimal viable products, to identify potential obstacles to practical implementation at an early stage, incorporate customer experience and evaluate internal implementation requirements. This results in a well-founded recommendation on the feasibility of the business idea. The leap over the biggest hurdle has been taken. Based on the insights gained many times over, companies achieve a perfect finish on their path to innovation.





